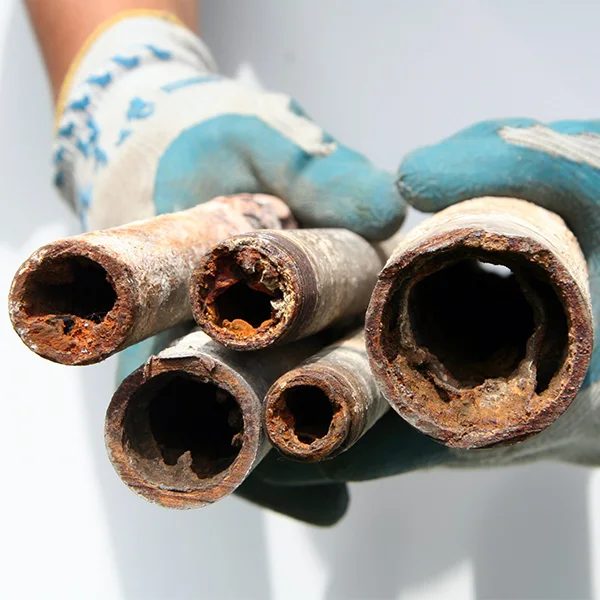
Scale deposits from hard water can clog water supply pipelines, increasing maintenance costs.
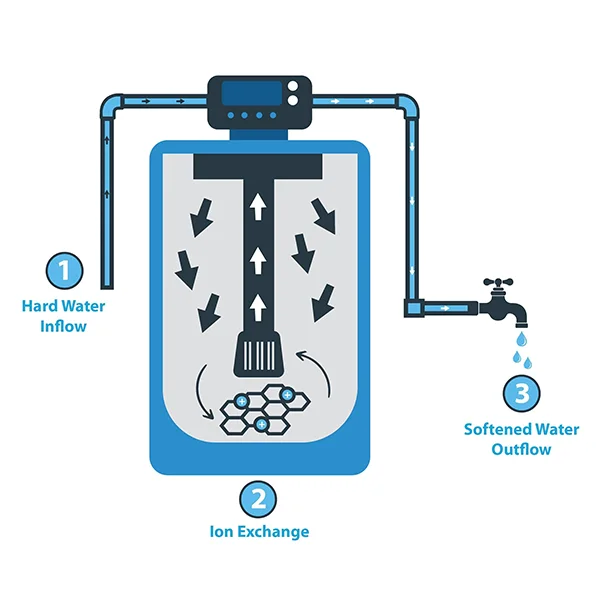
Water Softener is a device specifically designed to reduce water hardness. It converts hard water into soft water by removing calcium and magnesium ions, thereby preventing the formation of scale and improving the water consumption experience. Water softeners are widely used in homes, hotels, factories, and other places, especially popular in areas with hard water.
In daily life, the tap water we use usually contains a certain amount of minerals, such as calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions. When the content of these minerals is high, the water is referred to as hard water. Although hard water poses no direct harm to human health, it can cause many inconveniences and problems in daily life.

Scale deposits from hard water can clog water supply pipelines, increasing maintenance costs.
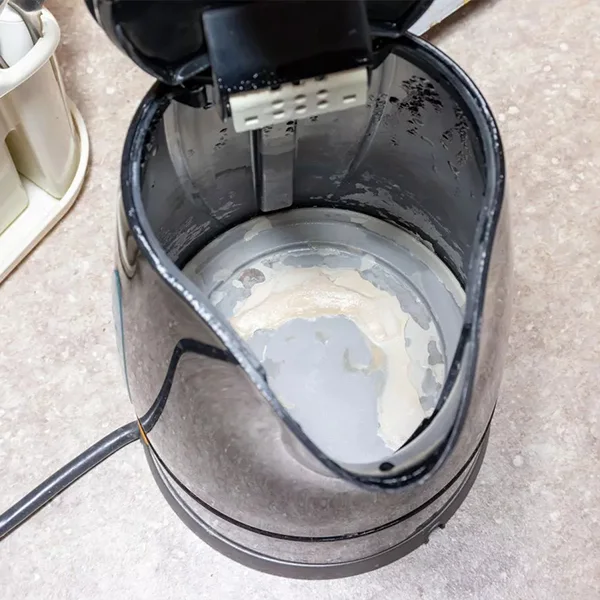

Hard water tends to form scale during heating, affecting the efficiency of water heaters and other equipment.
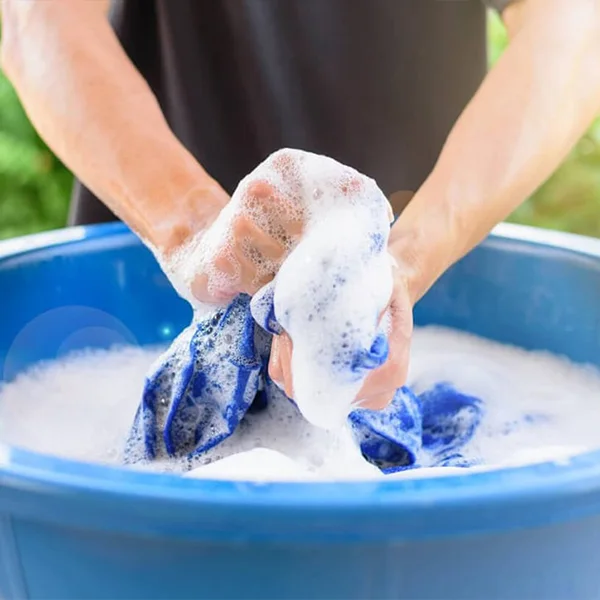

Hard water reduces the cleansing of soap and detergents, increasing their consumption.
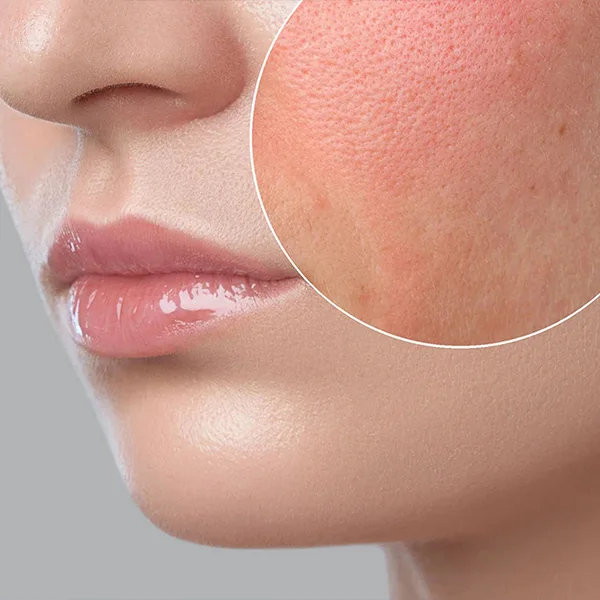
Mineral residues in hard water may cause skin dryness and roughness.
The use of a water softener can reduce water hardness, prevent scale formation, thereby protecting household appliances and pipelines, extending their lifespan, enhancing bathing comfort, and improving skin and hair conditions.
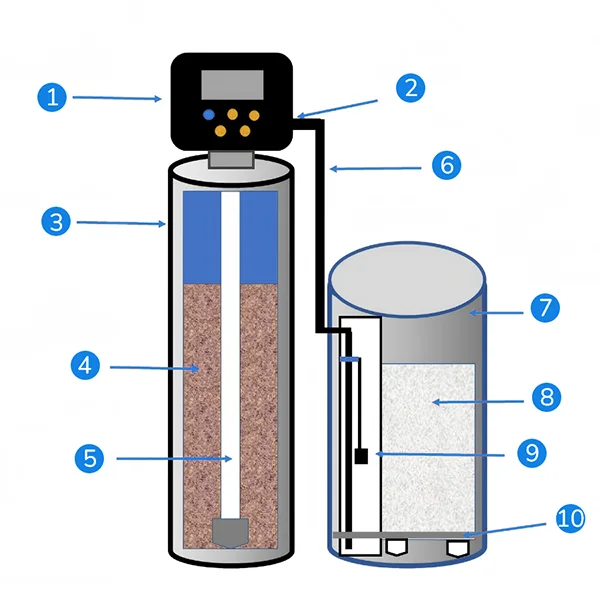
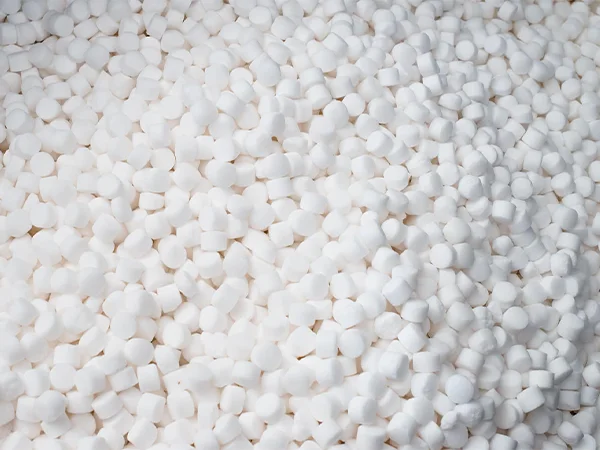
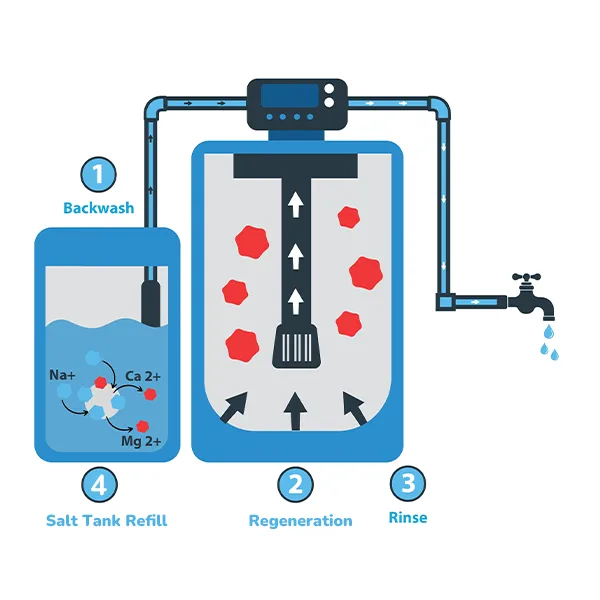
Water softener salt, also known as ion exchange resin regenerant, is primarily composed of sodium chloride (NaCl) with a purity of over 99.5%. During the operation of the water softener, water softener salt is required during the brine regeneration stage, and its quantity needs to be calculated based on the feed water hardness and the desired quality of the produced water. Since water softener salt is a continuously consumed water treatment material, it is necessary to ensure timely replenishment before the salt in the salt tank is completely depleted. It is recommended to add up to one-quarter of the salt tank's capacity to ensure normal operation of the equipment and maintain stable softening effects.